Question 10
Comments
- Though we are not asked for the value of
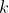 , it could be easily found as the total cumulative probability must be 1, and so
, it could be easily found as the total cumulative probability must be 1, and so  and the PDF can never be negative, which means that
and the PDF can never be negative, which means that  . Since we also know that
. Since we also know that 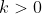 , there is only one possible value for
, there is only one possible value for 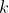 , which is
, which is  .
.
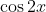 is an even function, and so the symmetry properties of this PDF will be the same as the standard normal distribution.
is an even function, and so the symmetry properties of this PDF will be the same as the standard normal distribution.- There is something wrong with this question.
Option
A is true because of the even symmetry.
Option
B is true for any PDF.
Option
C can only be true if both of the expressions given are

, because the given
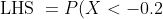)
and adding this gives the whole distribution with a total value of 1, and so it occurs at only one value... the question becomes, is that value 0.2?
 &=\cfrac{1}{3} \\ \int_a^{\infty} f(x)\ dx &= \cfrac{1}{3} \\ \int_a^{\frac{\pi}{4}} \cos{2x}\ dx + \int_{\frac{\pi}{4}}^{\infty} 0\ dx &=\cfrac{1}{3} \\ \left[\cfrac{1}{2}\sin{2x}\right]_a^{\frac{\pi}{4}} + 0 &= \cfrac{1}{3} \\ \cfrac{1}{2}\left[\sin{2\left(\cfrac{\pi}{4}\right)} - \sin{2a}\right] &= \cfrac{1}{3} \\ \sin{\left(\cfrac{\pi}{2}\right)} - \sin{2a} &= \cfrac{2}{3} \\ 1 - \sin{2a} &= \cfrac{2}{3} \\ \sin{2a} &= \cfrac{1}{3} \\ a &= 0.169918... \end{align*})
So, option
C is false as it is actually
 = P(-0.1699 < X < 0.1699))
Option
D can only be true if both of the expressions given are

, because the LHS + RHS covers half the distribution, and so they must add to

, which also occurs at only one value... and so the question again becomes, is that value 0.2?
 &=\cfrac{1}{4} \\ \int_a^{\infty} f(x)\ dx &= \cfrac{1}{4} \\ \int_a^{\frac{\pi}{4}} \cos{2x}\ dx + \int_{\frac{\pi}{4}}^{\infty} 0\ dx &=\cfrac{1}{4} \\ \left[\cfrac{1}{2}\sin{2x}\right]_a^{\frac{\pi}{4}} + 0 &= \cfrac{1}{4} \\ \cfrac{1}{2}\left[\sin{2\left(\cfrac{\pi}{4}\right)} - \sin{2a}\right] &= \cfrac{1}{4} \\ \sin{\left(\cfrac{\pi}{2}\right)} - \sin{2a} &= \cfrac{1}{2} \\ 1 - \sin{2a} &= \cfrac{1}{2} \\ \sin{2a} &= \cfrac{1}{2} \\ 2a &= \cfrac{\pi}{6} \\ a &= \cfrac{\pi}{12} \approx 0.261799... \end{align*})
So, option
D is false as it is actually
 = P(0 < X < 0.2618))
I have two problems with this question... the first is that there are two correct answers, unless I have made a mistake in looking at A and B. The second is that actually finding the boundaries for where expressions like those in C and D become true is a lot to ask in time and effort if there was not an obvious correct answer in A or B, starting with finding the only possible value for
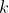
.
